This vignette provides an overview of the main functions in
litterfitter
Getting started
At the moment there is one key function which is
fit_litter which can fit 6 different types of decomposition
trajectories. Note that the fitted object is a litfit
object
fit <- fit_litter(
time = c(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6),
mass.remaining = c(1, 0.9, 1.01, 0.4, 0.6, 0.2, 0.01),
model = "weibull",
iters = 500
)
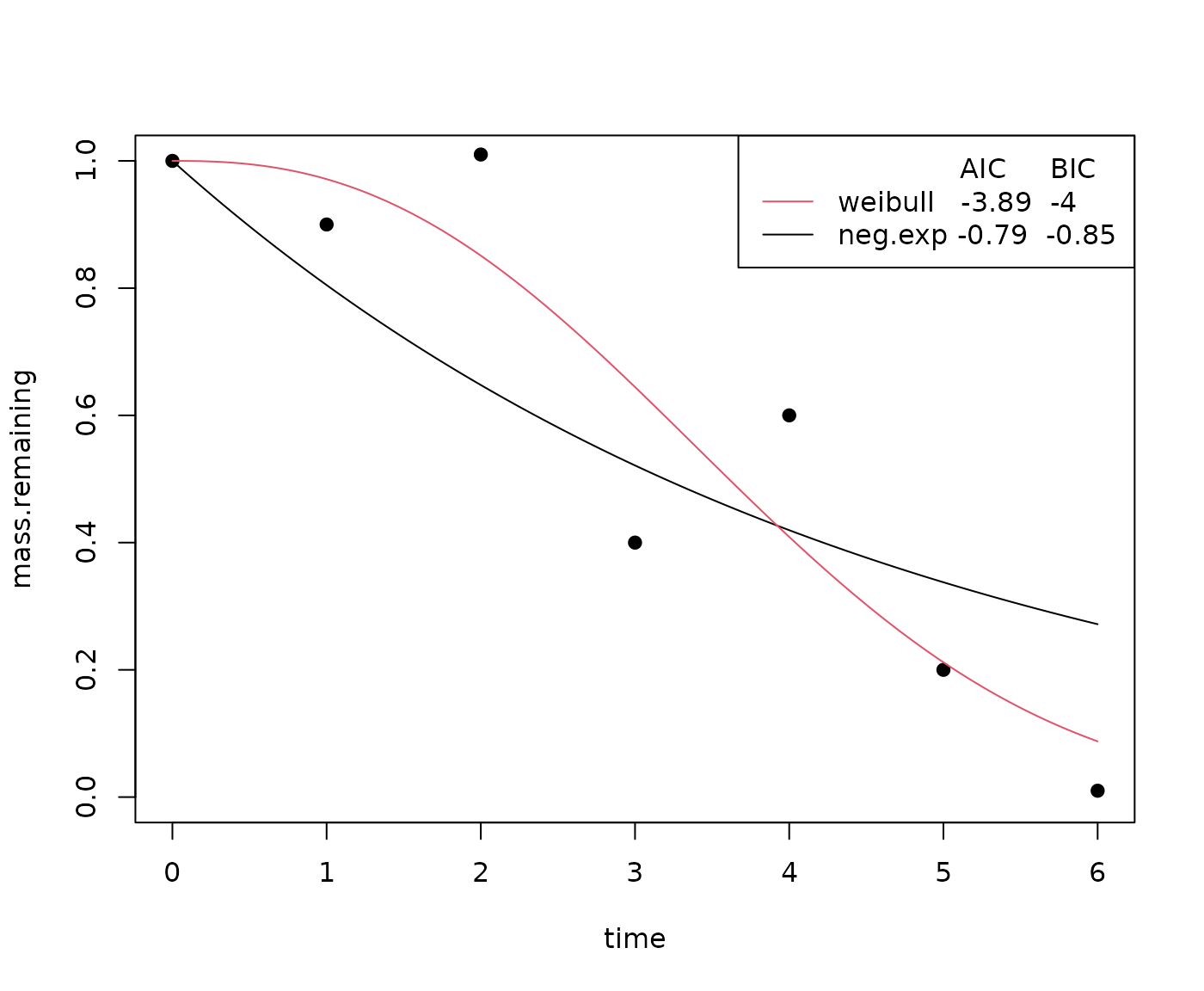
class(fit)You can visually compare the fits of different non-linear equations
with the plot_multiple_fits function:
plot_multiple_fits(
time = c(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6),
mass.remaining = c(1, 0.9, 1.01, 0.4, 0.6, 0.2, 0.01),
model = c("neg.exp", "weibull"),
iters = 500
)
Calling plot on a litfit object will show
you the data, the curve fit, and even the equation, with the estimated
coefficients:
plot(fit)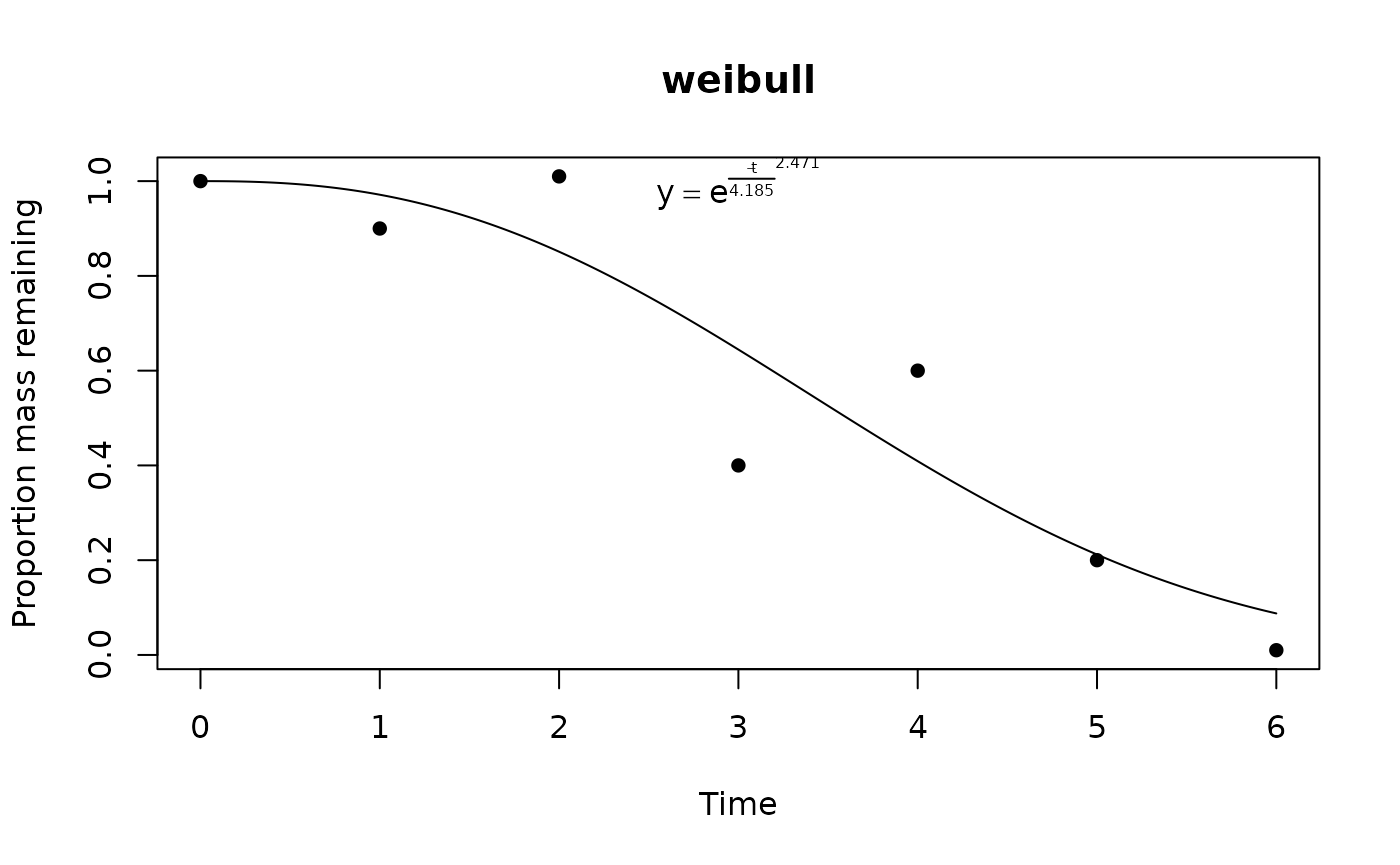
The summary of a litfit object will show you some of the
summary statistics for the fit.
#> Summary of litFit object
#> Model type: weibull
#> Number of observations: 7
#> Parameter fits: 4.19
#> Parameter fits: 2.47
#> Time to 50% mass loss: 3.61
#> Implied steady state litter mass: 3.71 in units of yearly input
#> AIC: -3.8883
#> AICc: -0.8883
#> BIC: -3.9965From the litfit object you can then see the uncertainty
in the parameter estimate by bootstrapping
